Using Responders and the Responder Chain to Handle Events 번역
04 Jul 2018 | iOSResponder Chain에 대해서 공부하다가 애플 개발자 문서에 있는 article을 번역하여 정리해보았다. 개인 공부용으로 매우 rough하게 번역하고 정리한 글이라 오역 많을 수 있음!
Using Responders and the Responder Chain to Handle Events
- 앱은 responder 객체를 이용하여 이벤트를 핸들링한다.
- responder객체는 UIResponder클래스의 인스턴스이고, 공통적으로 UIView, UIViewController, UIApplication객체를 서브클래스한다.
- Responder는 이벤트 데이터를 받거나 처리하고, 아니면 다른 responder객체로(해당 이벤트를 해결할 수 있는)전달해야한다.
-
앱이 이벤트를 받으면 UIKit은 가장 적절한 first responder에게 이벤트를 보낸다.
- 처리되지 않은(Unhandled)이벤트는 responder chain에 의해서 responder객체로 전달된다.
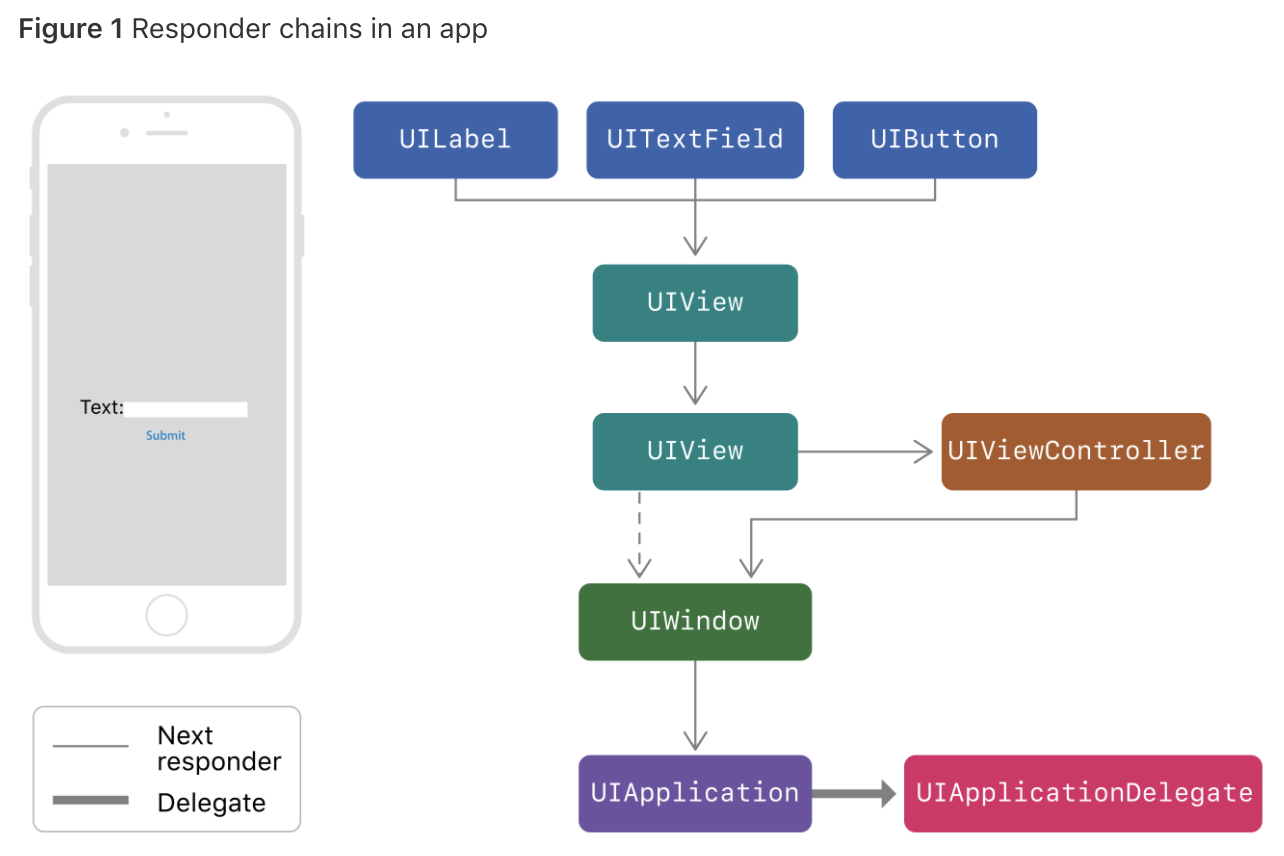
- 만약 텍스트필드가 이벤트를 핸들링하지 않으면, UIKit은 이벤트를 상위 UIView로 보낸다.
- 윈도우까지 이벤트가 전달됐음에도 이벤트를 핸들리할 수 없으면, 이벤트는 UIApplication까지 전달되며, and possibly to the app delegate if that object is an instance of UIResponder and not already part of the responder chain….??
이벤트의 first responder결정하기
UIKit은 이벤트의 타입에 따라서 FirstResponder 객체를 지정한다.
- Touch event: 터치가 일어난 뷰
- Press event: 포커스를 가진 뷰(The object that has focus.)
- Shake-motion event: 내가 지정한 객체 (The object that you (or UIKit) designate.)
- Remote-Control event: 내가 지정한 객체 (The object that you (or UIKit) designate.)
- Editing menu messages: 내가 지정한 객체 (The object that you (or UIKit) designate.) 리모트컨트롤이랑 editing menu가 뭐지..
cf) Core Motion Framework
Motion events related to the accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometer do not follow the responder chain. Instead, Core Motion delivers those events directly to the designated object. For more information, see Core Motion Framework
- 컨트롤은 자신들과 관련된 타겟 객체와 액션 메시지를 주고받는다.
- 컨트롤의 타겟 객체가 nil일때, UIKit은 올바른 액션 메소드가 구현된 객체를 찾아서 타겟 객체부터 responder chain까지 지나다닌다…탐색한다…찾아다닌다…?
- For example, the UIKit editing menu uses this behavior to search for responder objects that implement methods with names like cut(:), copy(:), or paste(_:).
- Action messages are not events, but they may still take advantage of the responder chain.
- GestureRecognizer는 touch나 press 이벤트를 자신의 뷰보다 먼자 받는다
- 만약 뷰의 GestureRecognizer가 터치 시퀀스를 인식하지 못하면, UIKit은 뷰에 해당 터치이벤트를 보낸다.
- 만약 뷰가 터치를 핸들링 하지 못하면, UIKit은 Responder chain에 이벤트를 보낸다.
어떤 Responder가 터치 이벤트를 가져야 하는지 결정하기
- UIKit은 어디서 터치 이벤트가 일어났는지 알기위해 뷰 기반의 hit-testing을 사용한다.
- UIKit은 뷰 계층구조에 있는 뷰들의 bound의 위치를 비교하며 터치의 위치를 비교한다.
- hitTest()메소드는 뷰 계층구조를 가로지르면서, 가장 깊은 단에 있는 서브뷰를 탐색하면서 특정 터치를 포함한 서브뷰를 찾아낸다.
- 터치 로케이션이나 다른 파라미터가 변경되면, UIKit은 똑같은 UITouch 객체를 새로운 정보와 함께 업데이트한다.
- (만약 터치 위치가 원래 뷰를 벗어나도, 터치객체 내의 view 프로퍼티는 변하지 않는다.)
- 터치가 끝나면 UIKit은 UITouch객체를 릴리즈한다.
Responder Chain을 바꾸기
- next 프로퍼티를 오버라이딩 함으로써 리스폰더체인을 변경 할 수 있다.
- (When you do this, the next responder is the object that you return.)
- UIKit 클래스들은 이미 이 프로퍼티를 오버라이드하여 특정한 객체를 리턴하여 이미 이 프로퍼티를 구현해놨다.
-
UIView objects. If the view is the root view of a view controller, the next responder is the view controller; otherwise, the next responder is the view’s superview.
- UIViewController objects.
-
If the view controller’s view is the root view of a window, the next responder is the window object.
-
If the view controller was presented by another view controller, the next responder is the presenting view controller.
-
-
UIWindow objects. The window’s next responder is the UIApplication object.
- UIApplication object. The next responder is the app delegate, but only if the app delegate is an instance of UIResponder and is not a view, view controller, or the app object itself.
-


Comments